
An Overview of the NVM Express® (NVMe®) Technical Proposal Ratification Process
BlogBy: Mike Allison, Sr. Director NAND Product Planning – Standards, Samsung, and Chair of the NVM Express Errata Task Group
Since the release of the NVMe 2.0 specification, over 60 technical proposals (TPs) have been ratified into the NVMe family of specifications, including Flexible Data Placement, Boot Specification, Cross Namespace Copy and more. Each newly ratified TP expands NVMe technology’s capability to meet industry needs and address challenges across the hyperscale and enterprise data center ecosystem.
The NVMe family of specifications is constantly expanding to add important new features for NVMe devices. With the ongoing evolution of NVMe technology, it’s essential that those interested in learning more about the NVMe specifications understand the TP ratification process and how it impacts the existing specifications.
NVMe Specification Ratification Process
The NVM Express TP ratification process consists of three phases, driving an initial TP from a basic technical concept into a refined and revised feature that expands the NVMe family of specifications. Through the ratification process, NVM Express member companies, the Technical Working Group (TWG) and the Board of Directors each contribute to the TP review cycles. Additionally, each phase concludes with a voting process from the TWG and the Board to determine if the TP is prepared to move into the next phase of ratification.
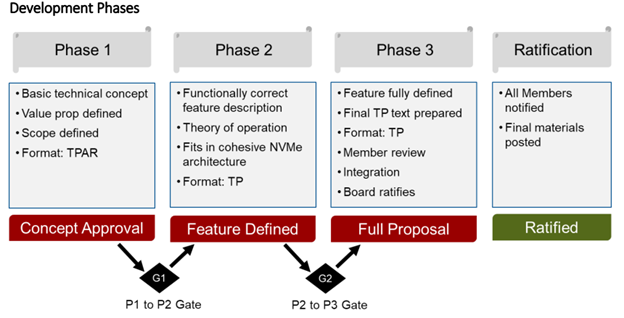
Phase 1
The initial phase is designed to determine the intended value proposition and overall scope of the TP, essentially highlighting the purpose of the feature if it were to be included in the NVMe family of specifications.
Phase 2
Phase 2 is intended to fully build out the functionality of the TP and demonstrate the capabilities of the feature, ensuring that it fits within the NVMe architecture.
Phase 3
Next, Phase 3 takes the fully defined TP and finalizes its inclusion in the NVMe family of specifications. After this stage, the TP is ratified.
Ratification
When a TP is ratified, it is treated as part of the NVMe family of specifications, however, it is managed as a separate document with any future changes to the TP being aggregated within that document. Any changes made to that TP are added as a lettered version of the document. For example, TP 4095 was updated to TP 4095a to include future additions. Those interested in finding the most up-to-date information on a TP should read the latest lettered version, which would be the newest version.
Specification Version Update
Finally, when an updated version of a larger NVMe specification is released, that latest version includes all of the TPs that were ratified as part of the previous specification version. All separate TP documents then only apply to any previous version of the specification, with future changes being made within the newest version of the specification.
Learn More
If you are interested in learning about the latest NVMe specifications and TPs, I highly recommend that you become a member of NVM Express. NVM Express members receive access to an integrated version of the latest NVMe specifications, which includes the most recent version of the specification and all the information regarding newly released TPs and Engineering Change Notices (ECNs), reducing much of the time needed to grasp the overall specification. I also encourage you to read more about the latest NVM Express specifications to find out the important features enabled by NVMe devices.
Additionally, As part of my “What’s New in NVMe® Technology: Ratified Technical Proposals to Enable the Future of Storage” presentation during the NVM Express sponsored speaker track at Flash Memory Summit (FMS) 2023, I provided an overview of the technical proposals (TPs) that have been ratified since FMS 2022.